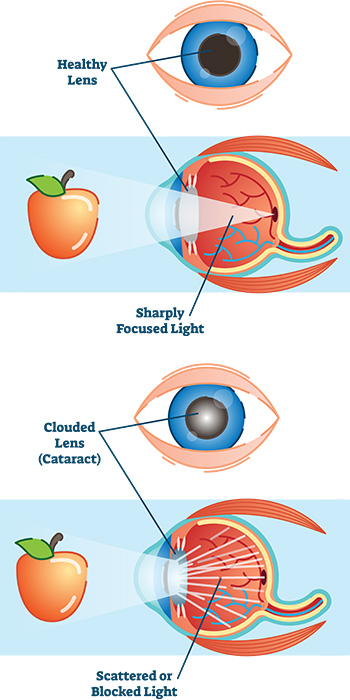
A cataract is a clouding of the natural lens in the eye and the leading cause of vision loss in adults over 55 years of age. Symptoms of cataracts include foggy or blurry vision, natural colours appear muted. You may also experience difficulty reading and driving, decreased night vision and halos around lights.
Cataracts can happen in one or both eyes and is closely related to aging, but may be accelerated by diabetes or eye trauma. However, a cataract is NOT a “film” over the eyes and CANNOT be cured by drops, diet or laser.
Most cataracts develop slowly and may not disturb your eyesight early on. At first, stronger lighting and eyeglasses can help you deal with cataracts. However, due to the clouding of the natural lens in your eye, if impaired vision interferes with your usual activities, you might need cataract surgery. Fortunately, cataract surgery is generally a safe and effective procedure.
Most cataracts develop slowly and may not disturb your eyesight early on. At first, stronger lighting and eyeglasses can help you deal with cataracts. However, due to the clouding of the natural lens in your eye, if impaired vision interferes with your usual activities, you might need cataract surgery. Fortunately, cataract surgery is generally a safe and effective procedure.
Risk and Prevention of Cataracts
Factors that increase your risk of cataracts include:
- Increasing age
- Diabetes
- Excessive exposure to sunlight
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Previous eye injury or inflammation
- Previous eye surgery
- Prolonged use of corticosteroid medications
No studies have proved how to prevent cataracts or slow the progression of cataracts, although, doctors think several strategies may be helpful, including:
Have regular eye examinations. Eye examinations can help detect cataracts and other eye problems at their earliest stages. It is a good practice to ask your doctor how often you should have an eye examination.
Quit smoking. Ask your doctor for suggestions about how to stop smoking. Medications, counselling and other strategies are available to help you through this process.
Manage other health problems. Follow your treatment plan if you have diabetes or other medical conditions that can increase your risk of cataracts.
Choose a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables. Adding a variety of colourful fruits and vegetables to your diet ensures that you’re getting many vitamins and nutrients. Fruits and vegetables have many antioxidants, which help maintain the health of your eyes.
Wear sunglasses. Ultraviolet light from the sun may contribute to the development of cataracts. Wearing sunglasses that block ultraviolet B (UVB) rays when you’re outdoors is recommended.
Reduce alcohol use. Excessive alcohol use can increase the risk of cataracts
Signs and Symptoms of Cataract
- Cloudy, blurred or dim vision
- Increasing difficulty with vision at night
- Sensitivity to light and glare
- Need for brighter light for reading and other activities
- Seeing “halos” around lights
- Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Double vision in a single eye

At first, the cloudiness in your vision caused by a cataract may affect only a small part of the eye’s lens and you may be unaware of any vision loss. As the cataract grows larger, it clouds more of your lens and distorts the light passing through the lens. This may lead to more noticeable symptoms.
Treatments
When your prescription glasses cannot improve your vision, the only effective treatment for cataracts is surgery.
When to consider cataract surgery ?
Cataract surgery is indicated when your cataracts begin to affect your quality of life or interfere with your ability to perform normal daily activities, such as reading or driving at night. Cataract surgery is one of the safest and most effective surgical procedures.
What does the surgery entail ?
Cataract surgery is usually performed under local anaesthetic .
The patient is admitted for a “day – procedure”, without an overnight stay in hospital. The operation entails making a small incision in the cornea and inserting an instrument about the size of a pen into the eye to break up and remove the cloudy lens (phaco-emulsification).
The natural lens is then replaced by artificial lens called an intra-ocular lens (IOL).
Who will administer the anaesthetic ?
Dr Tessa Beningfield , an anesthetist who has worked with Dr Rajen Pillay for more than 15 years, will administer the local anesthetic during the procedure. Click here for more info regarding the anesthetic and what to expect.
These are the steps involved during a cataract surgery:

